
What Is Generative Engine Optimization (GEO) [Tips & Workflows To Do It]
The author's views are entirely their own (excluding the unlikely event of hypnosis) and may not always reflect the views of Moz.
Some marketers think that Generative Engine Optimization (GEO) is a buzzword with temporary hype. But that’s a mistake because LLM search is gaining momentum.
Many websites are losing clicks to Google’s AI Overviews, and LLM tools like ChatGPT, Gemini, and Perplexity are gradually changing how users search for information.
If you’re not optimizing for AI search, you’re missing out on potential traffic that could lead to conversion.
At Exposure Ninja, we’ve been experimenting with GEO across industries, testing what actually works to earn visibility in these new search platforms.
In this guide, I’ll break down the practical strategies we use to optimize for generative search and how you can replicate our process to improve your brand visibility in AI search features.
Power your SEO workflow with smarter AI insights

What is Generative Engine Optimization (GEO)
Generative engine optimization is a strategy to optimize your content for LLM tools like Google’s AI Overviews, ChatGPT, Gemini, Perplexity, and other generative models that surface answers instead of links.

While SEO focuses on search engines, GEO adapts your content to be cited, summarized, or featured inside AI-generated responses. To achieve this goal, your content needs to be structured so that large language models can process it.
You might also hear it called LLMO, GSO, or AI search optimization. They all aim to get your content featured in generative engines to answer user questions.
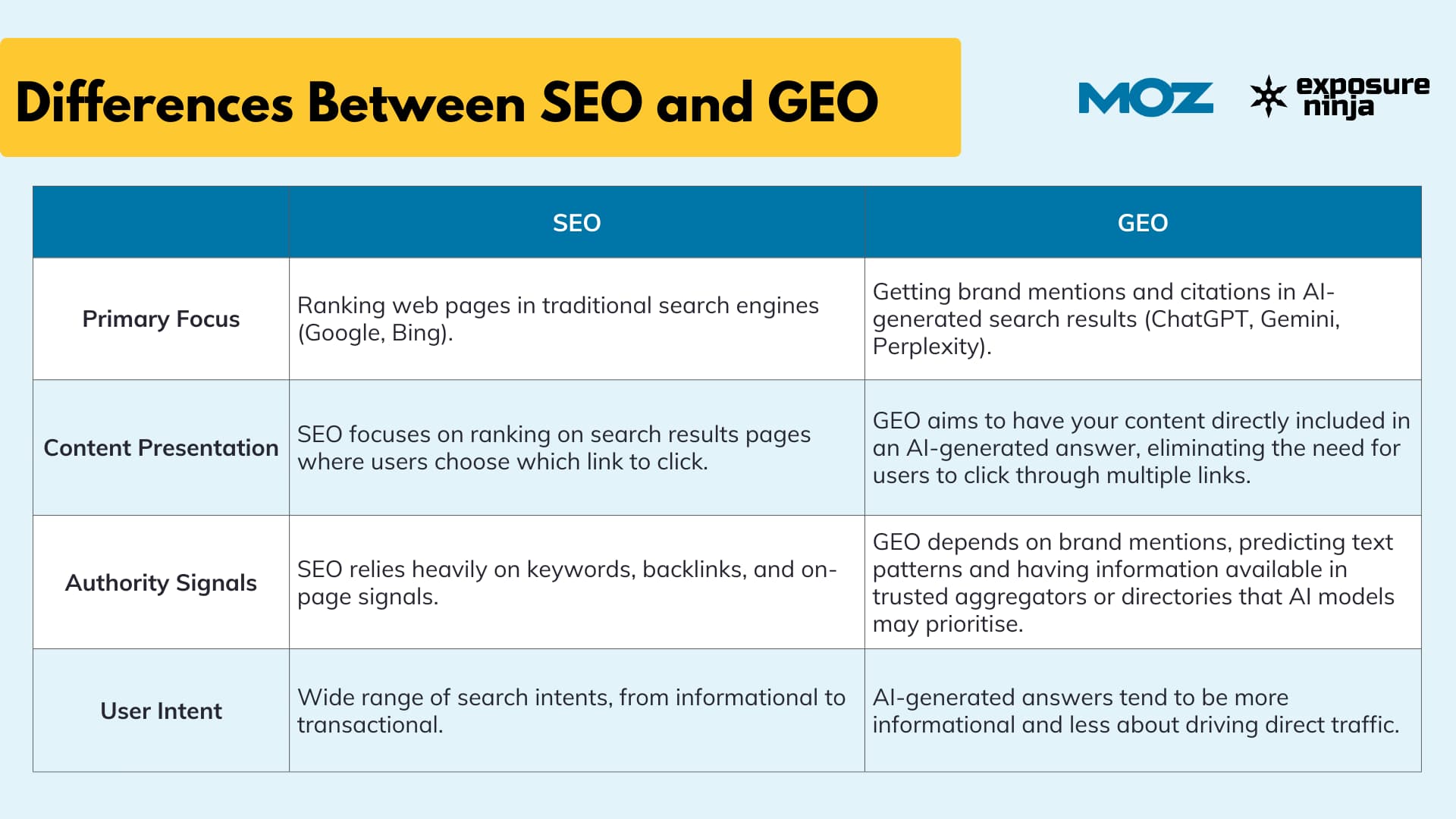
What is the difference between GEO vs. traditional SEO
While GEO builds on top of your existing SEO strategy, the signals you’re optimizing for and how you measure success are different.
Here’s how they compare:
How do generative engines work?
If you want your content to appear in generative search, you need to understand how these engines generate answers. Rather than just scanning for keywords, they break down the query to find the best sources and generate unique information each time.
Here's a quick video explaining how generative search engines work:
If you prefer text, I've got you covered below:
Generative engines rewrite the query
When you type a long, complex question into an AI tool like ChatGPT or Perplexity, it breaks the prompt into smaller, search-like queries and runs those through its model. That includes its internal training data and, depending on the engine, external sources like the web.
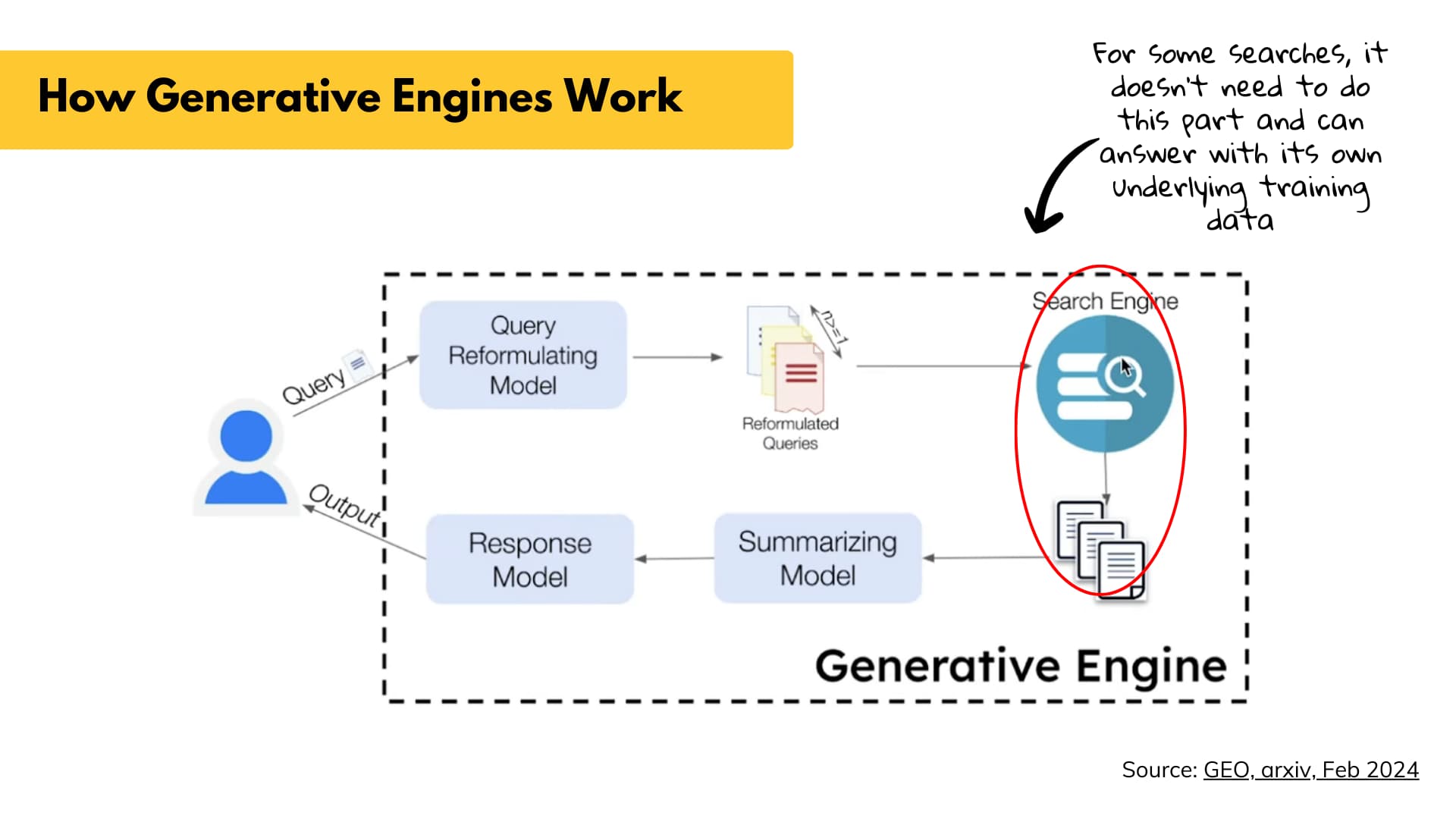
The model summarizes each result and then reassembles it into a response. Generative engines allow users to search with longer sentences, multiple trains of thought, or even entire paragraphs, as the model breaks down the input into chunks it can process.
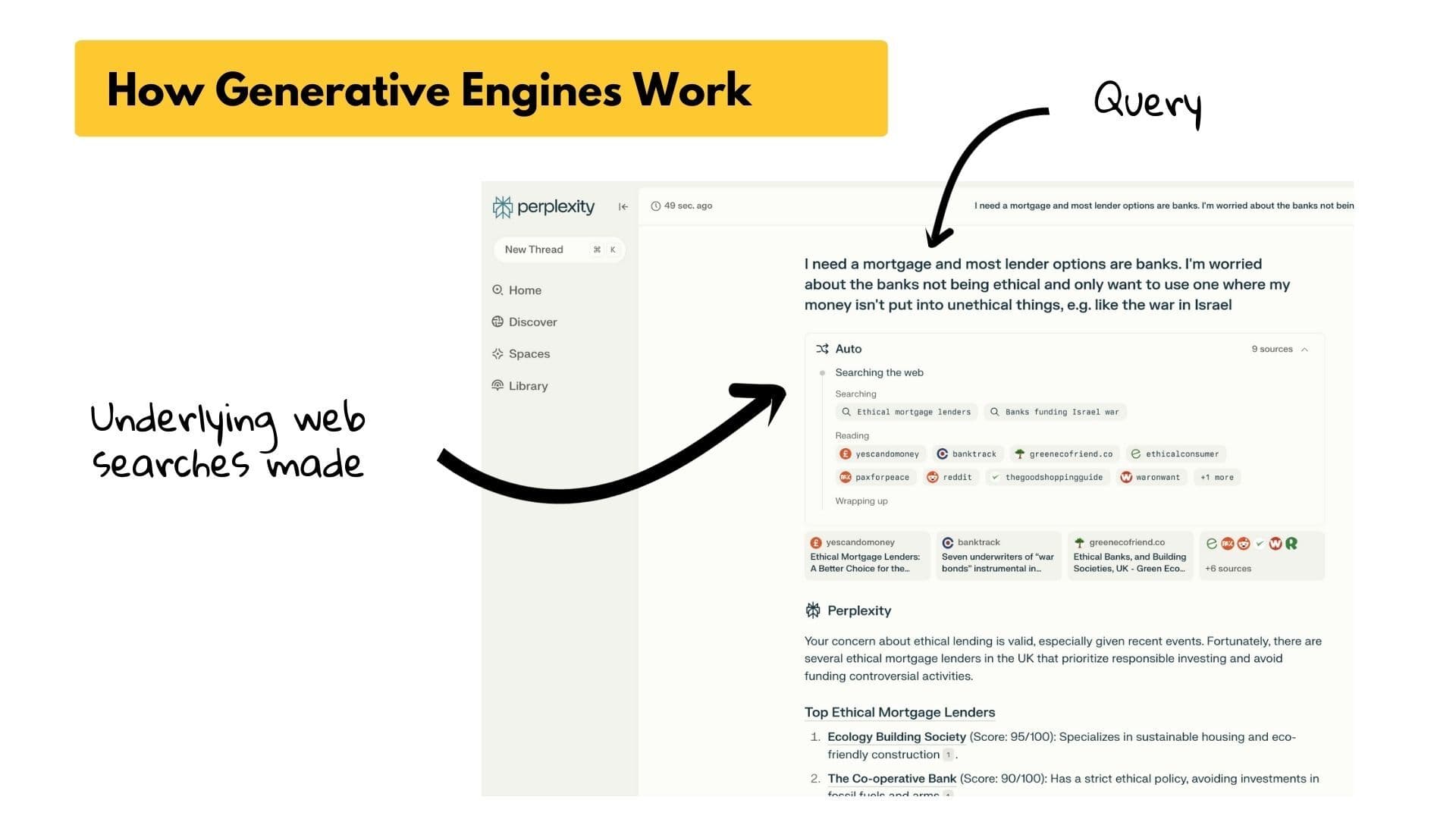
Perplexity is one of the few platforms that shows you what it’s doing under the hood. It runs multiple web searches in the background and cites sources directly in the output, making it easier to understand how information is gathered and used to form a final answer.
ChatGPT’s recently released o3 model is trained to “think” before generating answers, and it will show searchers what it’s thinking as it processes their query.
Provides different outputs based on the engine’s training and access
Not all generative engines work the same way. Some rely more heavily on web results, and others lean on pre-trained datasets. They also use different search engines or crawling methods behind the scenes. This is what we know right now about how these outputs are created by ChatGPT, Gemini, and Perplexity:
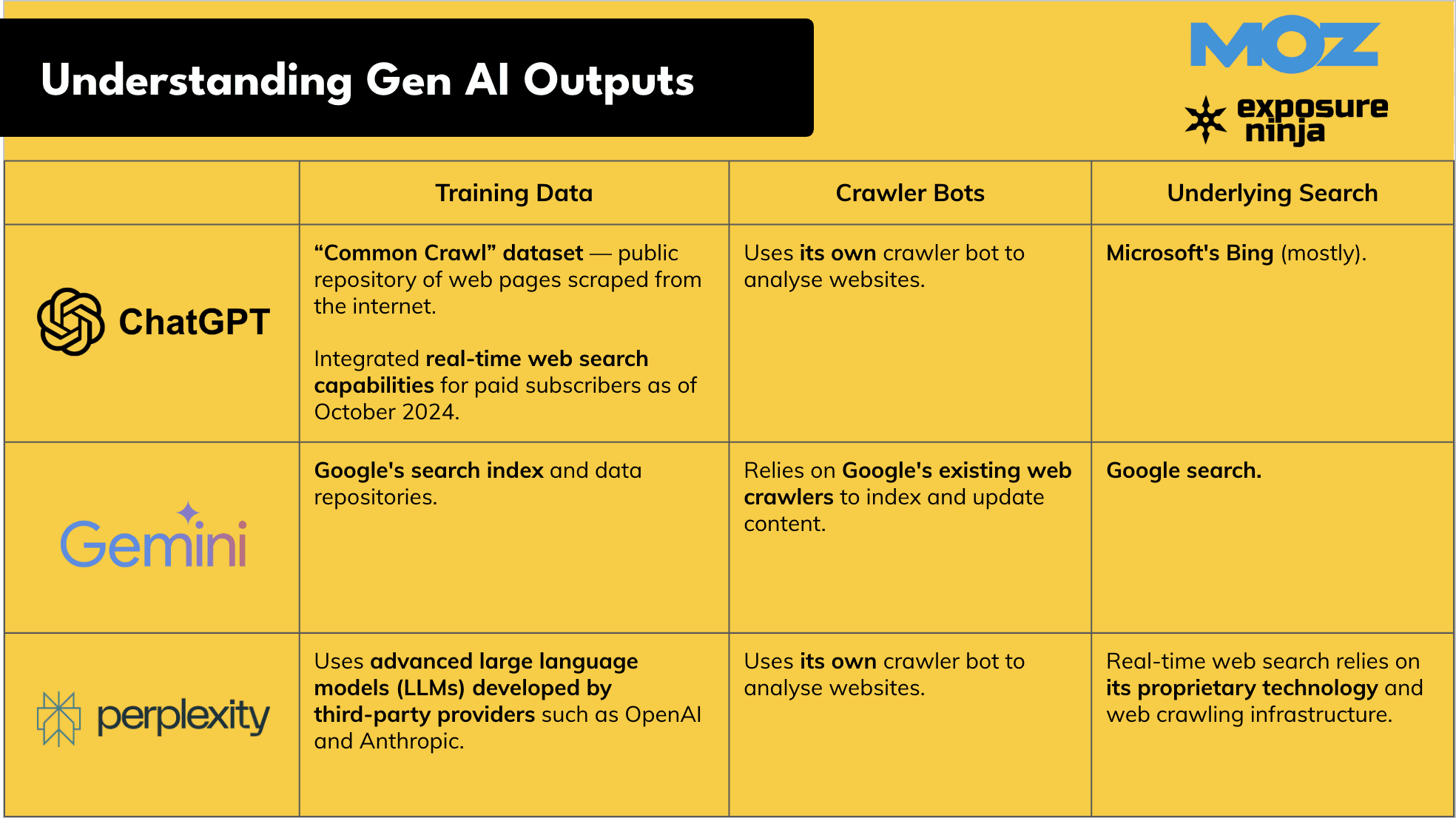
Since these engines use different data and methods to retrieve and summarize content, the same question may produce different answers depending on where you ask it.
Even when they cite sources, those citations will vary, so AI optimization needs to be broad enough to reach across platforms.
Outputs are generated, not copied
Generative engines don’t copy and paste responses from a database. They create new responses each time based on patterns in the data. They may reference the same page across multiple searches, but their language is generated on the fly.
When you turn on personalization, LLM engines like ChatGPT can tailor responses to your search history or preferences, adding even more variety to what’s returned.
See how Moz transforms your SEO with AI-powered insights

How to find opportunities to optimize for AI Overviews
If you’re already tracking organic rankings using STAT, you’re just a few filters away from uncovering AI Overview (AIO) opportunities. Here’s the workflow to identify opportunities to rank for AI Overviews:
Step 1: Find keywords already in the top 10 positions
Start by narrowing your dataset to keywords your site already ranks for in positions 1–10. This gives you a foundation of content close to winning, even if it hasn’t yet appeared in an AI Overview.
In STAT, go to your project view and filter for Top 10 rankings in your keyword set.

Step 2: Add the AI Overview SERP feature filter
Next, isolate the top 10 keywords that trigger an AI Overview by adding a SERP feature filter for “AI Overview”.
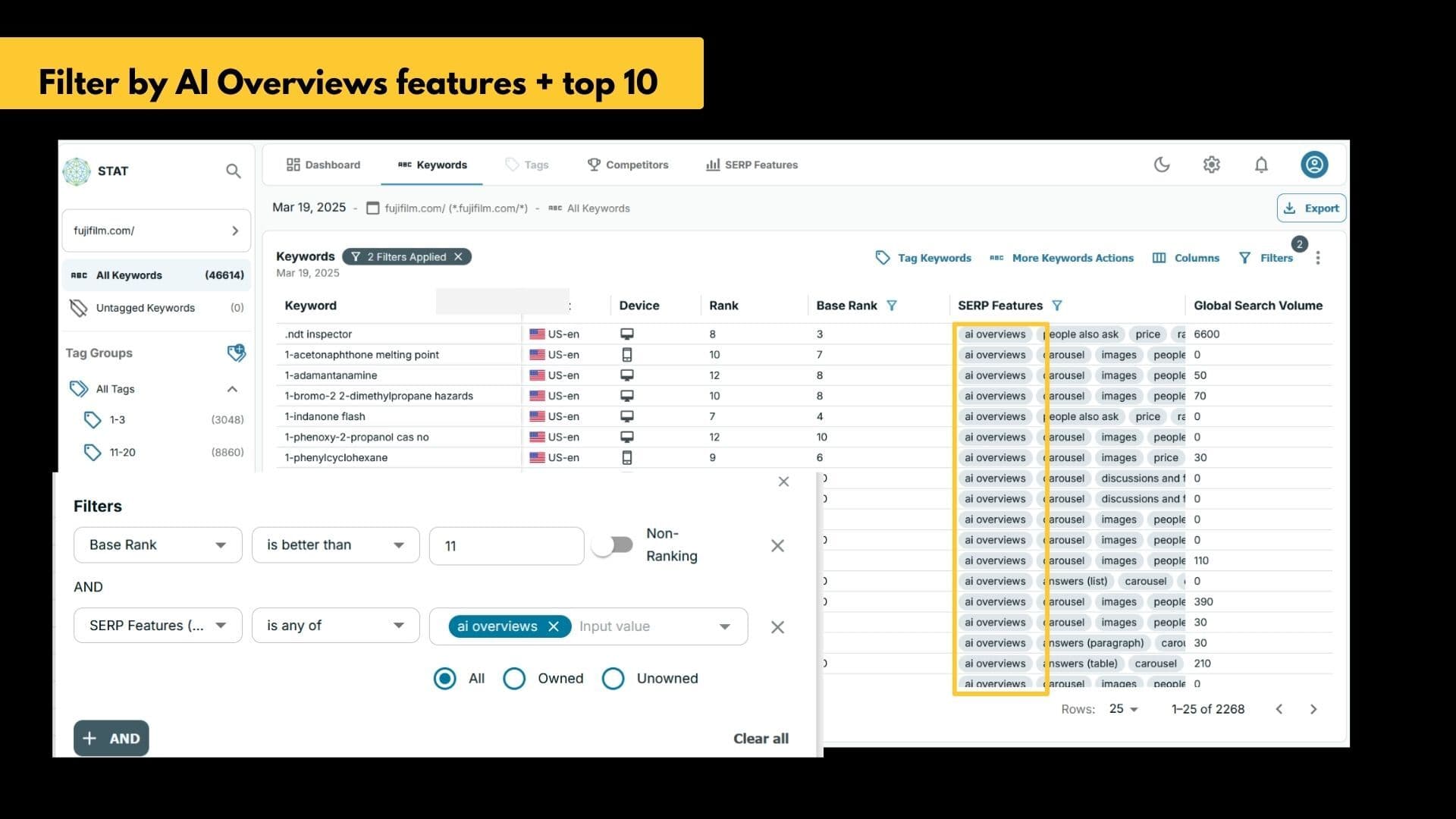
If your content is listed in the AI Overview, that’s great. If it isn’t, it’s an opportunity to optimize.
Step 3: Segment by owned vs. unowned AIOs
Now split your list into:
- Owned AIOs: Your content is being cited inside the AI Overview
- Unowned AIOs: An AI Overview exists, but your content isn’t included
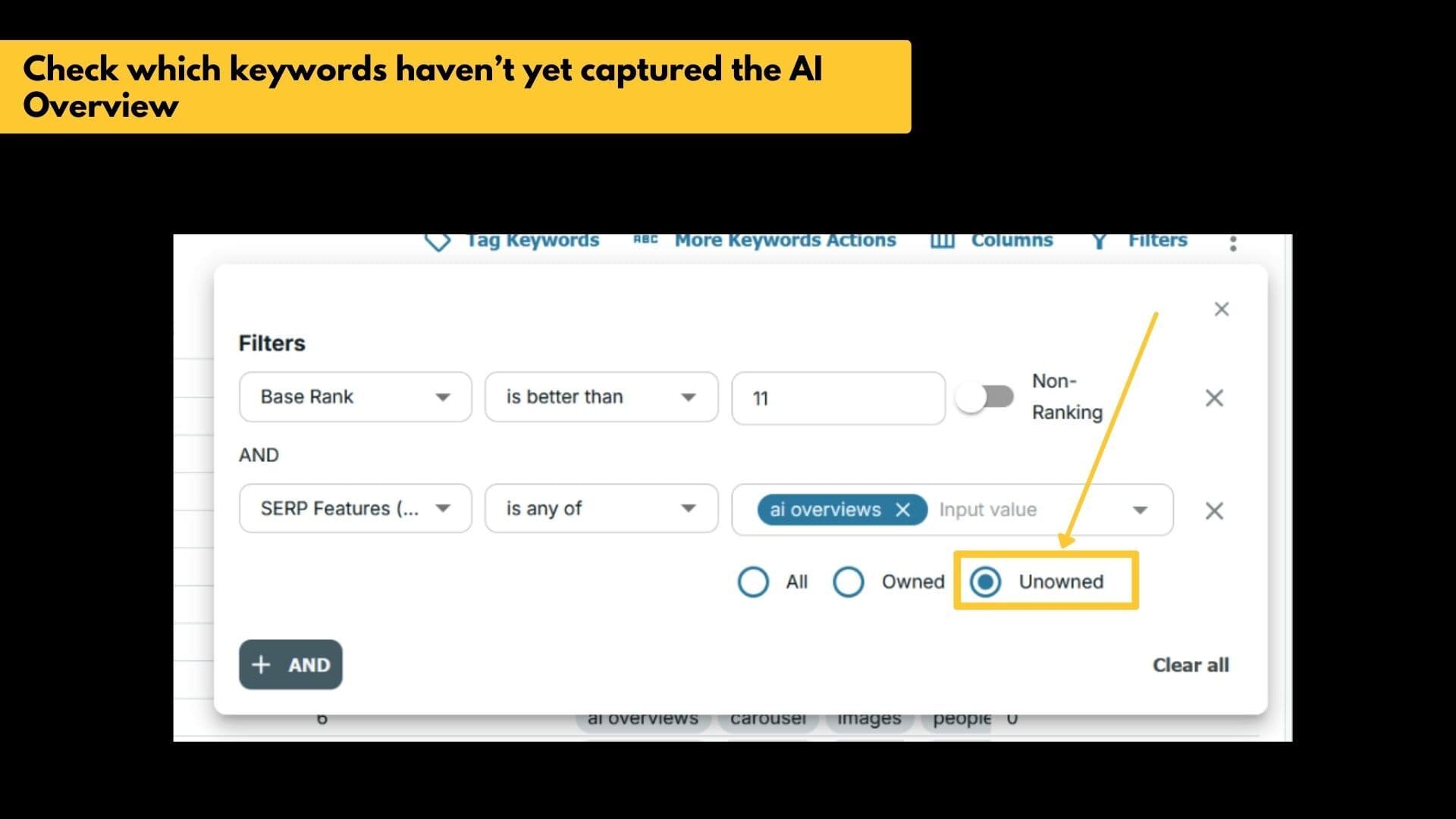
This helps you focus your energy on unclaimed opportunities where you’re already in the top 10, but not cited in the AI Overview summary.
Step 4: Prioritize high-value, commercial-intent queries
Create a list of target keywords to optimize for the AI Overview.

Focus on the ones tied to revenue:
- Keywords with buying or research intent
- Branded product or service queries
- Pages with high conversion potential
Tip: Look for overlap between unowned AIOs and your highest-value landing pages in GA4. These are prime targets for GEO optimization.
Track your search performance at scale
Whether you’re juggling multiple sites or millions of pages

How to appear in generative AI searches
Here’s the checklist we use at Exposure Ninja to help our clients earn citations inside AI results.
Extreme close matching
The first thing we do is closely match the information we publish with the phrase we’re trying to rank for.
For example, we wrote an article on “What is Digital PR” and noticed that the AI Overview text was taken from the introduction, where we included the keyword “digital public relations.”
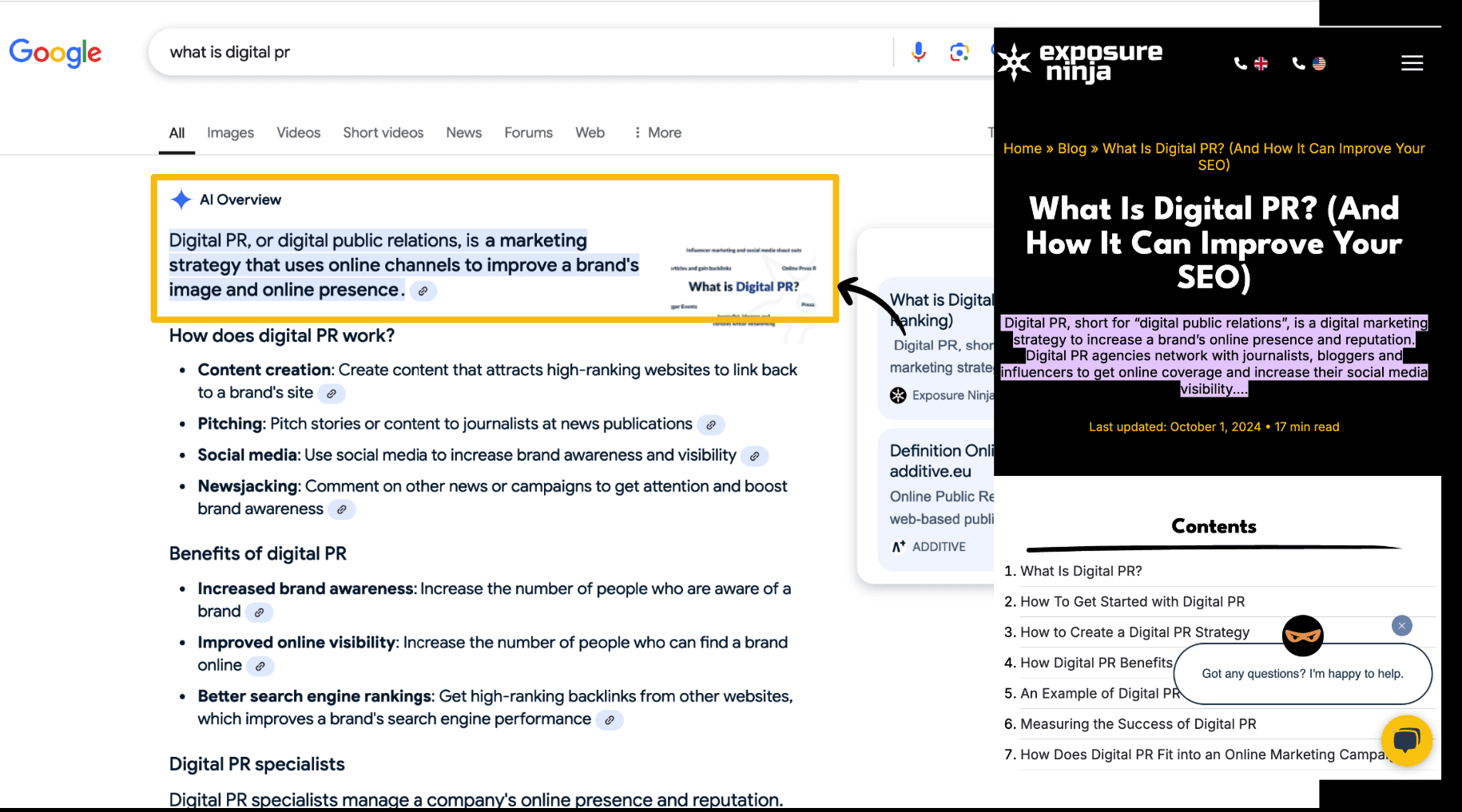
Answer questions directly and use bullet points to break down key information
Make sure your content is simple and easy to read. Just like people struggle to follow overly complex information, AI has a harder time understanding content that isn’t structured. It looks for recognizable patterns and direct language to interpret your message accurately.
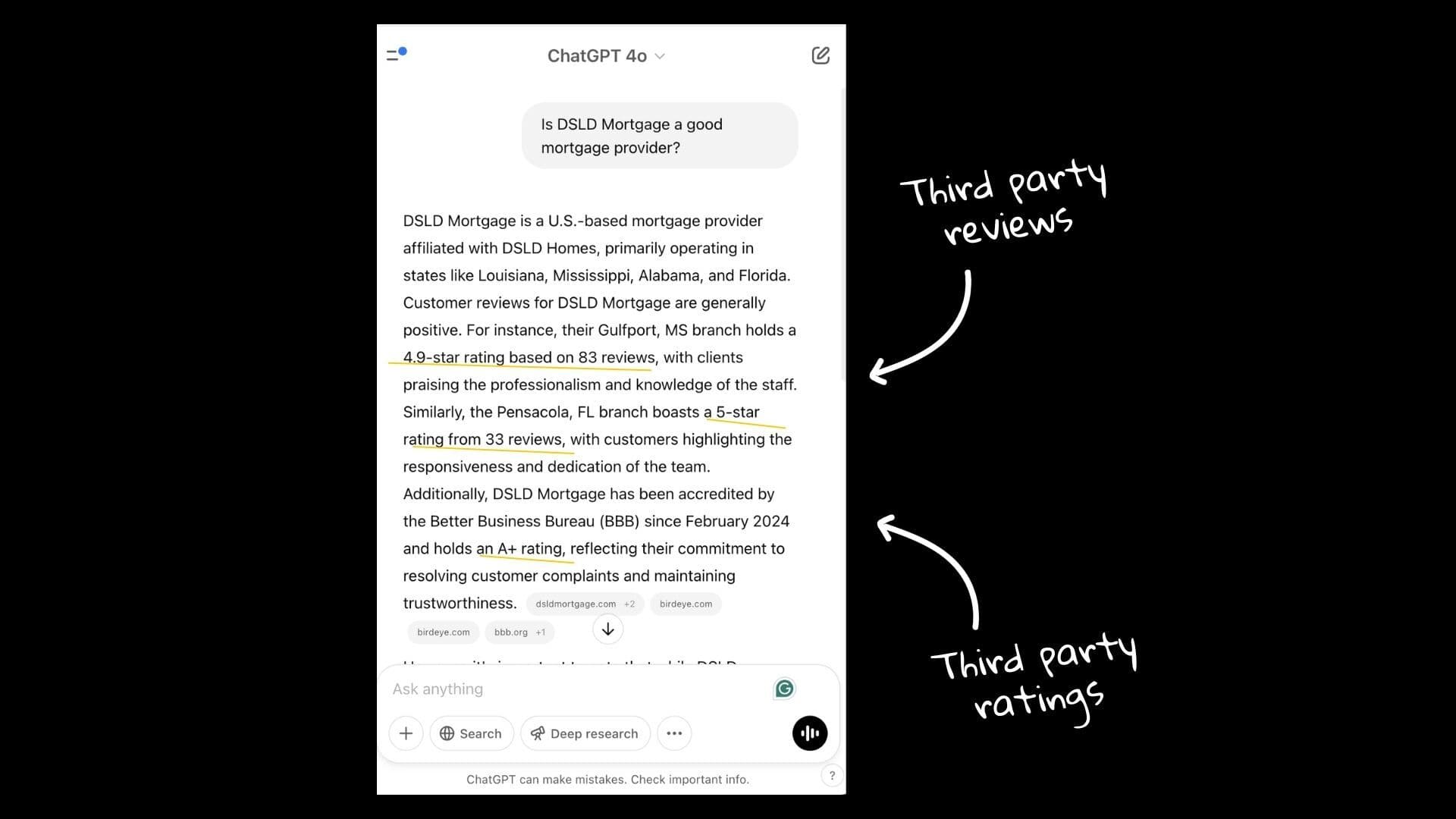
For example, in the screenshot below, we worked with DSLD Mortgage to create a guide on mortgage payments.

One of our biggest changes was rewriting the intro paragraphs to be straightforward and easy for AI to interpret.
We also structured key sections using bullet points to highlight specific takeaways we knew would align with common AI Overview questions. This helped us anticipate the types of follow-up queries users might ask.
We personalized the content by featuring a mortgage professional as the author, who wrote from a first-person perspective. The author’s expertise improved the E-E-A-T of the content, which is an important signal of quality content.
Here’s an excellent explanation from Moz on how to optimize content for E-E-A-T
Finally, we broke down information into simple formats, updated the schema, and ensured the page structure supported AI scraping.
Rank well in regular organic and local search
You need to be visible in traditional search to earn citations in generative search. Without that baseline, it’s unlikely your content will appear in AI Overviews or be referenced by generative engines.
Local SEO plays a key role here as well. Google’s map packs, business citations, and optimized service pages play a big role in getting picked up, especially in platforms like Gemini.
For example, when you search for McCallen personal injury lawyer, Patino Law Firm has the Google Map Pack for the keyword.
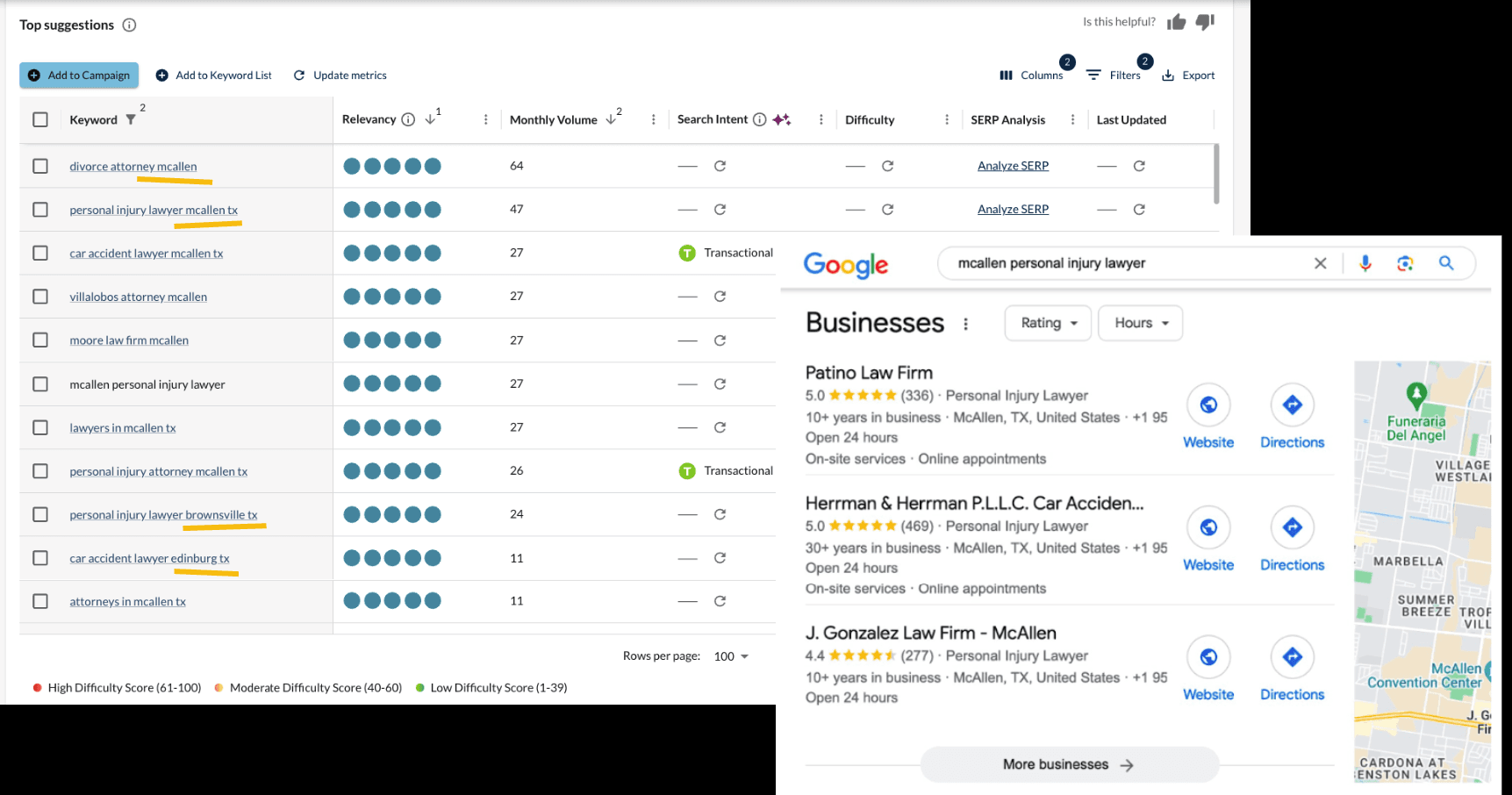
They are also showing up in Gemini for many related local search queries.
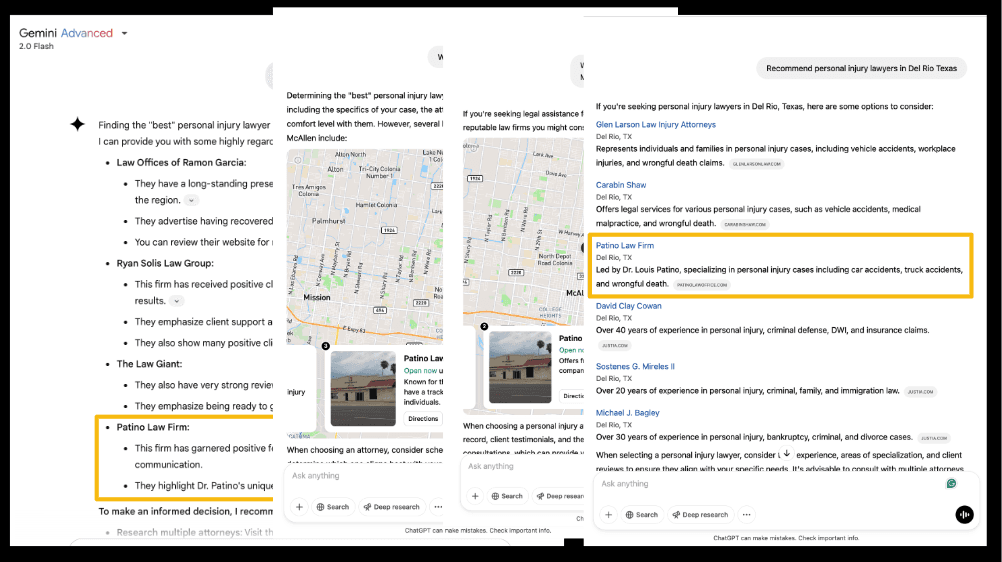
We believe Gemini pulls some data directly from Patino Law’s Google Business Profile, including location, contact info, and reviews.
This shows how an optimized Google Business Profile, positive third-party reviews, and local content can influence how you appear in generative responses.
Get cited as a data or research source
Generative engines prioritize information that feels authoritative, and that includes data. But what’s interesting is that the data source doesn’t always have to be the brand itself.

In one example pulled from ChatGPT, Unilever is cited in a conversation about microplastics. However, the study being referenced hasn’t even been published by Unilever. It’s a third-party research that mentions Unilever in a relevant context.
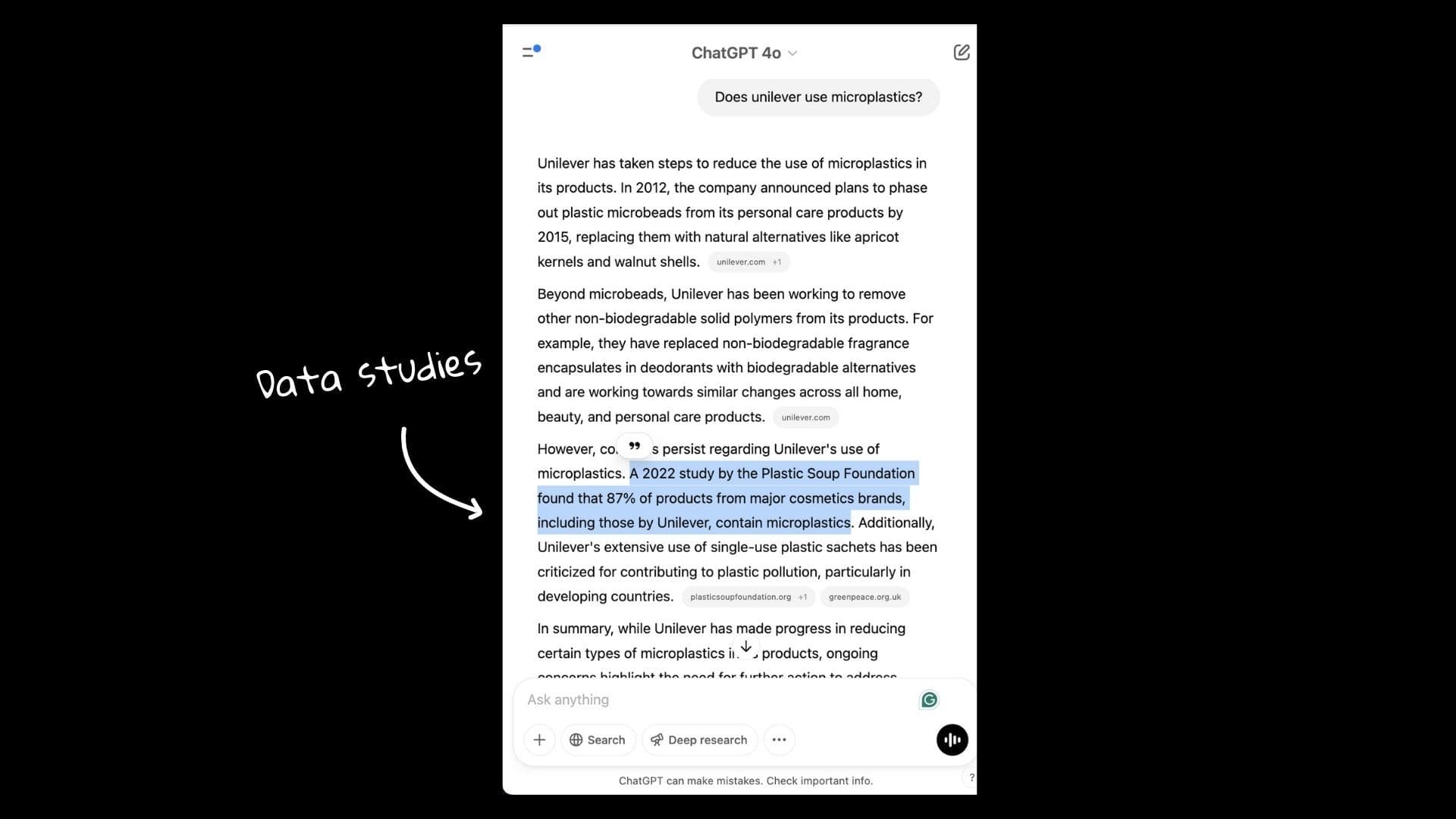
Because AI models value research content so highly, they often surface these types of citations above more conventional brand messaging.
The takeaway here is simple: if you want to influence how your brand appears in AI answers, you need to be associated with strong, well-evidenced research, even if you're not the one publishing it.
This includes:
- Commissioning or collaborating on third-party studies
- Earning coverage or quotes in existing data-led content
- Publishing your own research-backed thought leadership
As Steve Rayson once said in a Moz study, “If you want to create content that achieves a high level of shares and links, concentrate on opinion-forming, authoritative content that’s well researched and evidenced.”

The same holds true for GEO, where data, statistics, and independent validation help your brand get pulled into answers, especially when your site isn’t the most authoritative source in the traditional SEO sense.
Influence brand perception through PR and positioning
Some brands are already winning in generative search because of their positioning in media, third-party content, and user discussions.
A standout example is The Ordinary. For years, they’ve consistently owned two brand positioning phrases: “best value skincare” and “science-backed skincare.”
These phrases reflect how people naturally search and how competitors are framed. The Ordinary baked them into every touchpoint including press releases, product descriptions, interviews, and influencer campaigns.
These E-E-A-T signals and high-profile brand mentions contribute to how frequently The Ordinary shows up in AI search features.
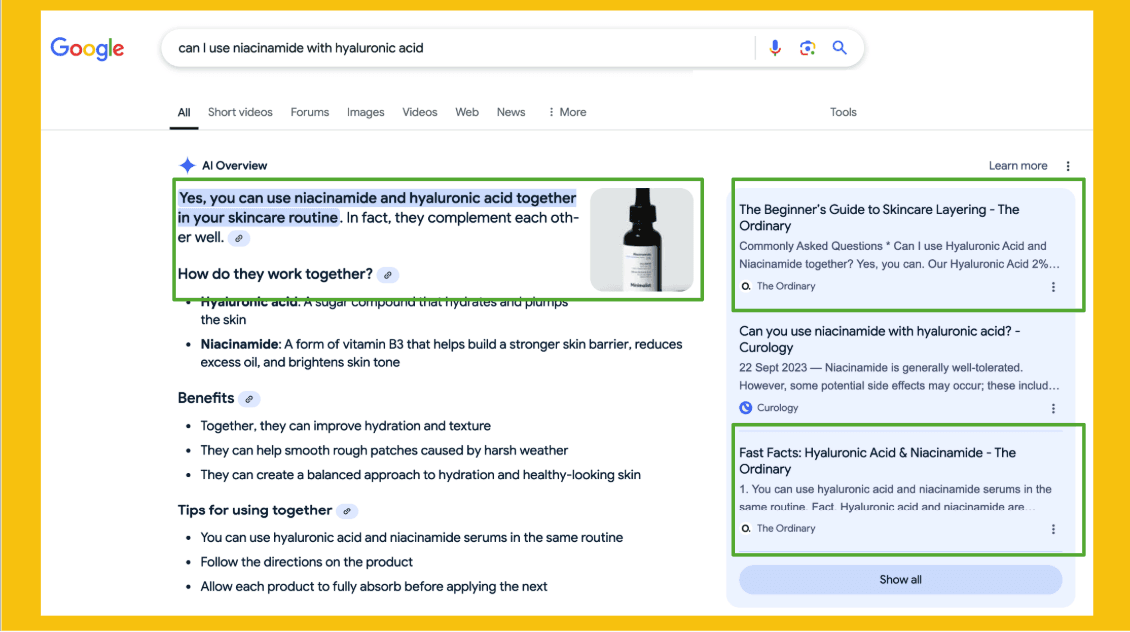
That pattern also extends to Reddit threads and blog content, where users echo the brand’s language in their discussions. This organic reinforcement, combined with sustained PR campaigns, helps the brand show up in AI-generated responses even when they’re not the source of the data.
To be clear, you don’t need to run PR for years to get similar results. What you need is a repeatable market positioning message and a strategy to spread it across trusted, indexable sources.
Here’s how to do it:
- Choose one or two key positioning phrases that align with search behavior
- Create messaging around those phrases in everything from author bios to boilerplate
- Pitch thought leadership and product roundups to media outlets already covering your space
- Use platforms like Reddit and Quora to surface community-led discussions about your brand and reinforce your positioning
What matters is that your brand is consistently described the same way, across platforms, by people and publications that LLMs already trust. If you can shape that perception, AI engines will carry it forward.
Power your SEO workflow with smarter AI insights

What metrics should you track for GEO?
You won’t find traditional keyword rankings in generative search. There’s no average position, SERP feature box, or impression metrics. But that doesn’t mean you can’t track GEO, it just requires a different approach.

Here’s how we track generative engine performance at Exposure Ninja and what you should be measuring.
Track your presence in AI Overviews
Start by identifying which of your target keywords trigger AI Overviews in Google. You can do this using tools like STAT to monitor owned and unowned AIO appearances.
Set up a custom campaign to track the number of AI Overviews you appear in and whether that number is increasing over time.
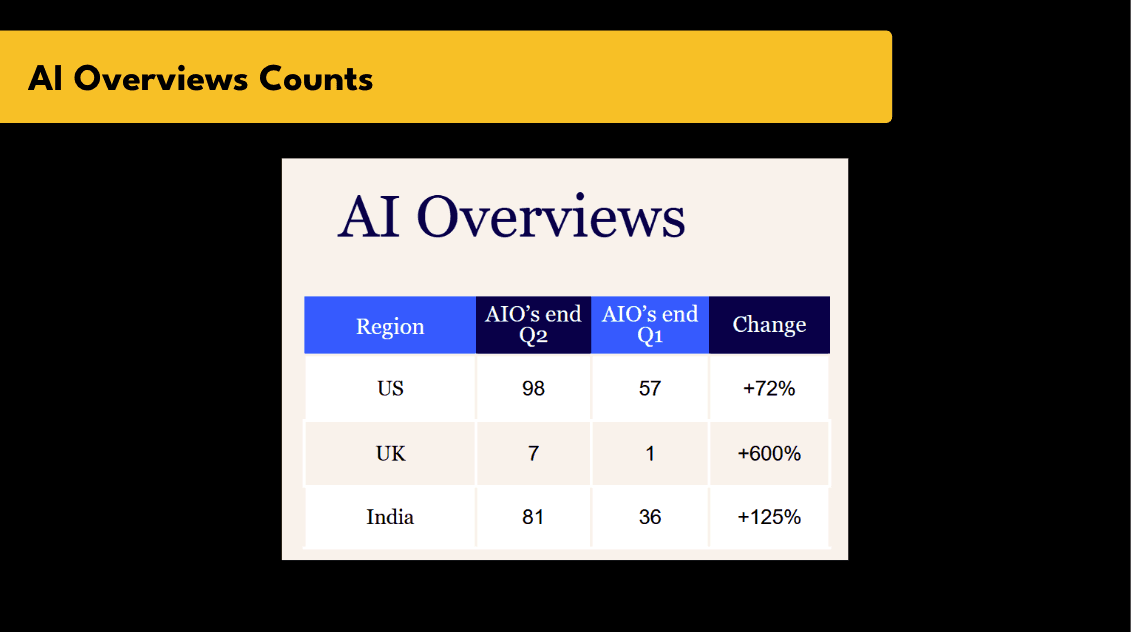
We do this manually for clients across priority regions, comparing coverage at the start and end of each quarter. It’s simple but highly effective.
Monitor referral traffic from AI platforms
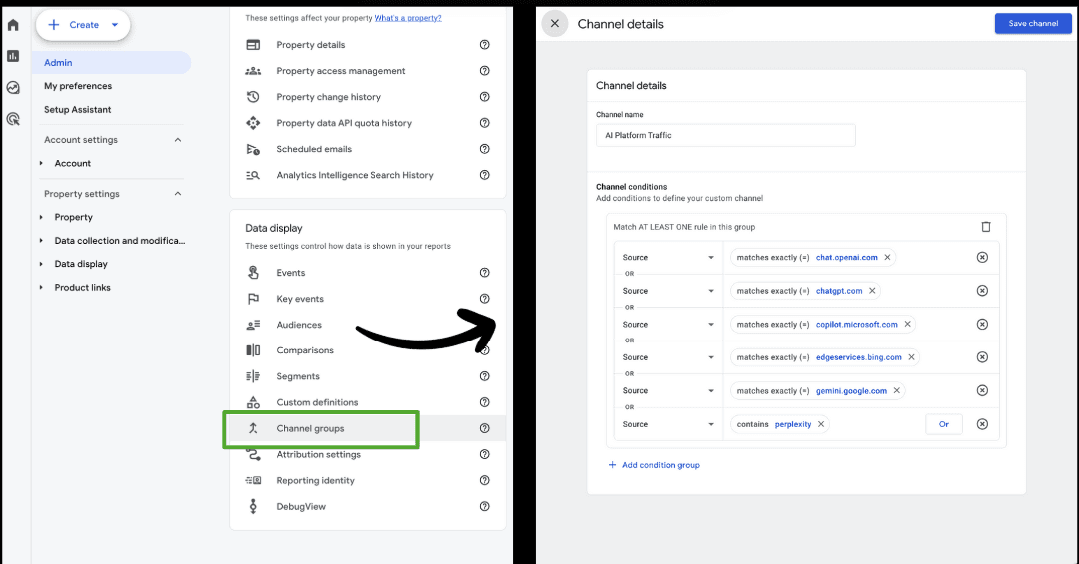
Use GA4 to filter and group traffic coming from ChatGPT, Bing, Gemini, and other AI engines.
In our workflow, we’ve created custom channel groups for each platform so we can track traffic sources separately and see where gains are coming from.
- Settings > channel group > add
- Drag it up to the top
- The list has to be updated if there is a new Gen AI platform
The setup lets us:
- Track total traffic from each AI engine
- Visualize performance trends over time
- Prioritize optimization based on what’s driving results
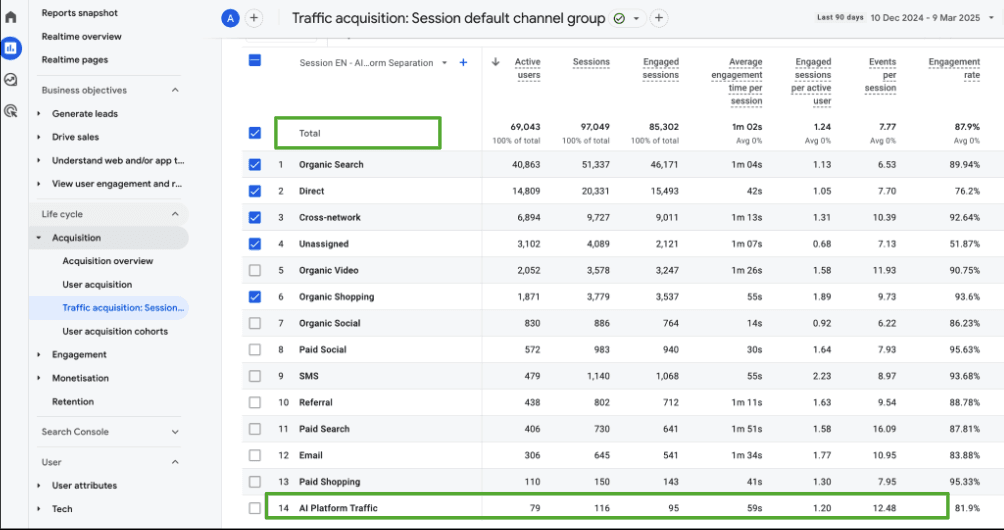
Don’t forget to increase your GA4 table row limits, as AI traffic often shows up toward the bottom by default.
Measure sessions and conversions from AI referrals
You can’t track specific keywords in generative search, but you can track outcomes. In Looker Studio, we surface GEO landing pages and show which AI platforms drive the most conversions.
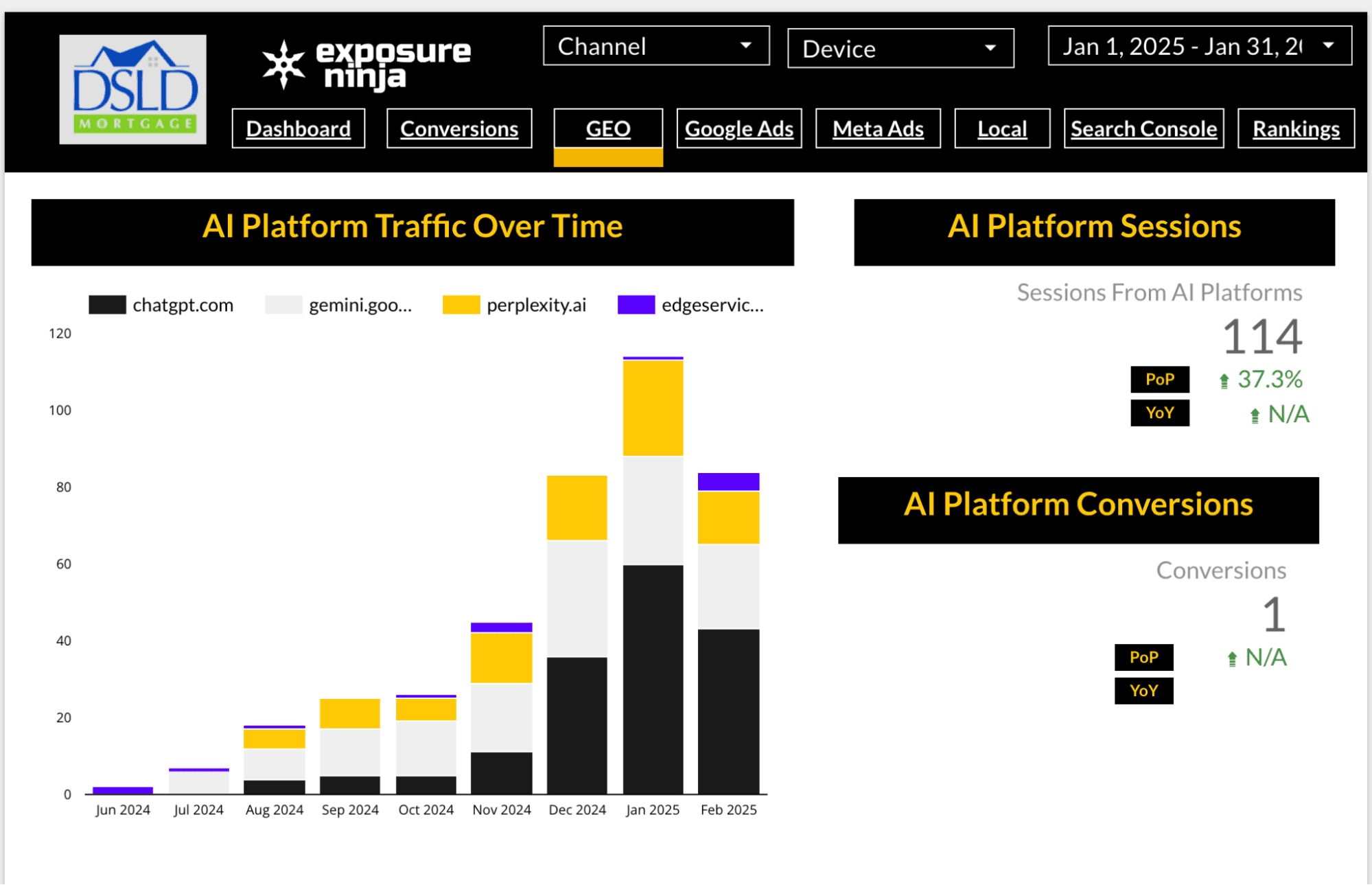
If most users are entering through the same URLs, that’s a signal that generative engines are referencing those pages. Segment these by platform to see whether ChatGPT, Perplexity, or another tool performs best and adapt your strategy accordingly.

In one client report, we found that 52% of all AI search traffic was coming from ChatGPT. That insight shifted our focus toward more LLM-friendly copy and formatting.
Analyze brand sentiment and accuracy in AI platforms
Beyond traffic, it’s important to understand how generative search platforms describe your brand and whether that information is accurate.
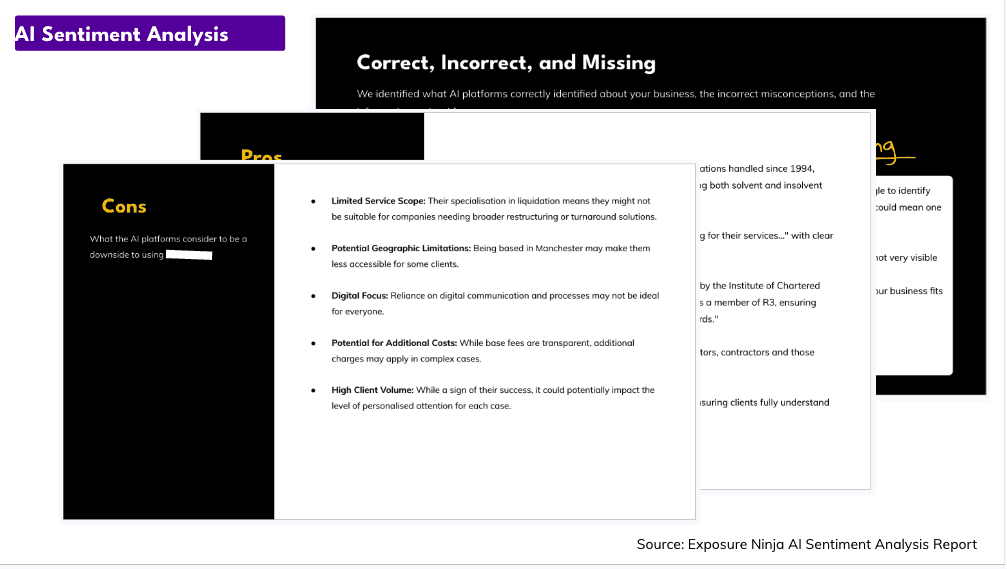
We run manual brand audits inside ChatGPT, Gemini, and Perplexity to check for:
- Correct or outdated descriptions
- Missing key product information
- Conflicting messages across platforms
This helps us spot areas for improving messaging, filling content gaps, or correcting misinformation before it spreads. For clarity, we summarize these findings in client-facing reports with example queries and screenshots.
See how Moz transforms your SEO with AI-powered insights

Mistakes to avoid when optimizing for generative search
Getting cited in generative engines doesn’t follow the same playbook as SEO. In fact, some tactics that work in traditional search won’t help your visibility in ChatGPT, Gemini, and Perplexity.
Here’s what to avoid:
Assuming SEO rankings equal AI visibility
Ranking well in Google doesn’t mean you’ll be featured in generative answers. AI engines use different inputs and are trained to identify patterns, not positions.
Using screenshots, diagrams, or product images as key answers
Visual elements rarely appear in AI chat results. Some platforms may pick up video, but images like charts and screenshots are rarely referenced. If the value you provide isn’t in the text, it probably won’t be seen.
Duplicating answers across your page and website
Repeating the same answer on a page (body of text and FAQ) or multiple pages can confuse large language models. It makes it harder for generative engines to detect relevance and intent.
Publishing high volumes of unedited AI content
AI engines don’t reward quantity. Unedited or templated content is more likely to be ignored or flagged as low value. Generative search relies on clarity and context. If your copy lacks both, it won’t make the cut.
Spamming LLMs with repeated brand mentions
Stuffing the same brand phrase into every content doesn’t improve your visibility. In fact, it can have the opposite effect. Generative engines look for natural signals across credible sources. Your tactics to increase Brand Authority should feel natural, not forced.
Relying on keywords instead of authority
If you only focus on keywords without building brand credibility, you won’t get much value from generative search platforms. As Chima Mmeje said in her spicy hot take, you need an integrated digital strategy that prioritizes brand and SEO, rather than silos.
Concluding thoughts: Start optimizing for generative engines today
You don’t have to choose between GEO or SEO when you can optimize for both. Use STAT to find AI Overview opportunities, invest in digital PR to increase brand mentions, and track the right performance metrics.



